Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil gotten from the fruit of the oil palms. Originally found in West Africa and grown only in tropical rain forests, oil palm trees are now grown across Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil gotten from the fruit of the oil palms. Originally found in West Africa and grown only in tropical rain forests, oil palm trees are now grown across Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Although Palm oil is primarily used for cooking, it is a major ingredient in a wide range of products such as food manufacturing products like margarine, chocolate, ice cream, and baking products. It is also used as biofuel and in the production of beauty products like lipsticks, deodorants, toothpaste, and shampoo.
The demand for palm oil continues to increase for a lot of reasons; it costs significantly less than other vegetable oils, it is very versatile and can be used widely for different purposes, it is also a very efficient crop that can produce high quantities of oil fruits over small areas of land. This makes it a highly productive and lucrative product for farmers.
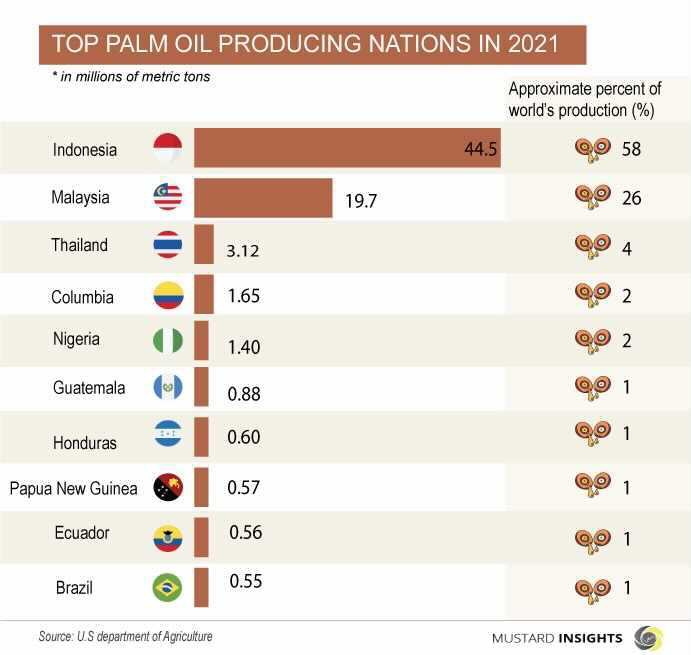
Although we can find palm oil in a variety of products that we use daily, it is produced majorly by two countries. According to the “United States Department of Agriculture”, Indonesia and Malaysia contribute about 84% of the total production of palm oil worldwide. In Indonesia and Malaysia together, approximately 4.5 million people earn a living from palm oil production.
Indonesia produced over 44.5 million metric tons of palm oil in 2021, 58% of the world’s palm oil production, making it the largest producer of palm oil.
Malaysia ranks 2nd position in palm oil production. Producing over 19.7 million metric tons of palm oil in 2021, this is approximately 26% of the world’s palm oil production.
Thailand in 2021, approximately contributed 4% of the world’s palm oil production by producing 3.12 million metric tons of palm oil. Countries like Columbia and Nigeria contributed 2% each by contributing 1.65 million metric tons and 1.40 million metric tons of palm oil respectively.
Other countries like Guatemala, Honduras, Papua New Guinea, Ecuador, and Brazil produce contribute approximately 1% each to the world’s palm oil production.
The impact of palm oil production on the environment is one of the challenges facing palm oil production. Deforestation where areas of tropical forests are cleared to make room for oil palm plantations causes the displacement of some endangered species like elephants, rhinos, and tigers from their natural habitat.
The burning of tropical rain forests to clear the area of oil palm plantations releases smoke, carbon dioxide, and greenhouse gas emissions leading to air pollution and contributing to climate change. Health consequences have been recorded throughout Southeast Asia because of the smoke and haze from these fires.
Other effects of oil palm production on the environment are soil erosion and pollution, water pollution, and climate change.
European Palm Oil Alliance (EPOA) and World Wild Life organization (WWF) are some of the organizations that believe that palm oil can be produced without putting the environment in danger. They believe that for the production of palm oil to be sustainable, the environmental and social issues centering on the forced labor of children and violation of human rights need to be addressed.
Thoughts?
We won't share your email address. All fields are required.
